What Is Scrum? | Scrum Methodology
Introduction:
In the realm of project management, Scrum has emerged as a popular and effective framework that promotes agility, collaboration, and iterative progress. Originally developed for software development, Scrum has found application in various industries due to its adaptability and focus on delivering value in a dynamic environment. This article aims to provide a detailed overview of Scrum, exploring its principles, methodology, roles, ceremonies, and benefits.
Understanding Scrum:
Principles of Scrum:
understanding "what is Scrum" operates on the foundation of several core principles:
Iterative Development: Work is divided into smaller, manageable tasks or increments called "sprints," typically lasting 2-4 weeks, allowing for continuous improvement.
Empirical Process Control: Scrum thrives on transparency, inspection, and adaptation. It encourages teams to regularly assess their progress and adapt to changing requirements.
Self-Organizing Teams: Teams are cross-functional and autonomous, responsible for managing their work and making decisions collectively to achieve sprint goals.
Customer Collaboration: Continuous feedback from stakeholders ensures alignment with customer needs and helps in delivering value-driven outcomes.
Scrum Methodology:
Scrum follows a structured approach that comprises three main components:
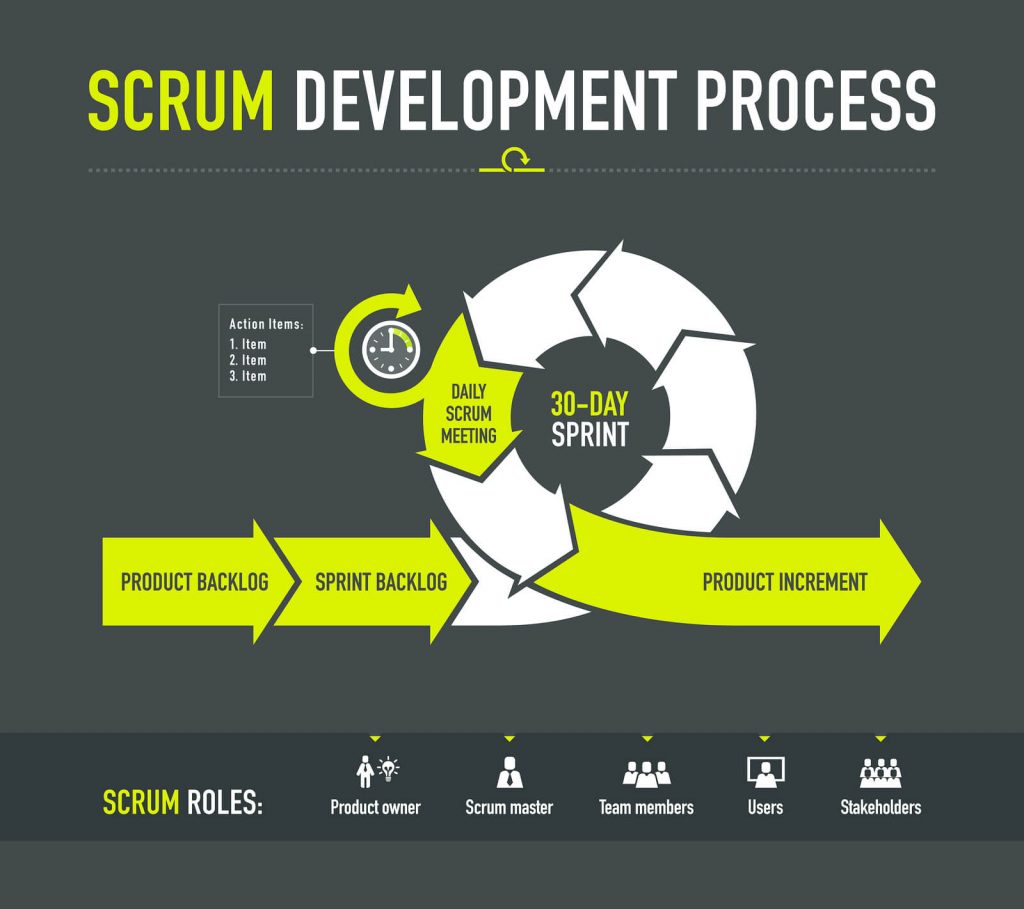
Roles: Scrum defines specific roles, including the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team. The Product Owner represents the stakeholders, prioritizes the product backlog, and ensures the team builds the right features. The Scrum Master facilitates the Scrum process, removes impediments, and supports the team. The Development Team consists of professionals responsible for delivering the product.
Artifacts: Key artifacts in Scrum include the Product Backlog (a prioritized list of features, enhancements, and fixes), Sprint Backlog (tasks to be completed in a sprint), and Increment (the sum of all completed work from a sprint).
Ceremonies: Scrum ceremonies ensure collaboration and transparency. These include Sprint Planning (determining what can be delivered in a sprint), Daily Stand-ups (short meetings to update on progress and plan the day), Sprint Review (demonstrating completed work to stakeholders), and Sprint Retrospective (reflecting on the sprint and identifying improvements).
Benefits of Scrum:
Flexibility and Adaptability: Scrum allows teams to adapt to changing requirements, fostering flexibility in the development process.
Enhanced Communication and Collaboration: Regular meetings and constant communication within the team and with stakeholders improve collaboration and alignment.
Faster Delivery: Incremental development ensures that usable product increments are delivered frequently, leading to quicker time-to-market.
Increased Product Quality: Continuous feedback loops and regular testing contribute to higher product quality and customer satisfaction.
Conclusion:
Scrum has become a leading methodology for agile project management, enabling teams to navigate complex projects efficiently. Its emphasis on adaptability, collaboration, and iterative development has made it popular across diverse industries beyond software development. By embracing the core principles and practices of Scrum, organizations can enhance their project delivery, foster innovation, and achieve better outcomes while responding adeptly to evolving market demands.

Comments
Post a Comment